Zusammenfassung
Künstliche Intelligenz (KI) ist keine Science-Fiction mehr – sie ist eine praxisorientierte Technologie, die das Leben, Arbeiten und Innovieren der Menschen verändert.
Dieser Leitfaden erklärt, was KI ist, wie sie aus Daten lernt und wie sie intelligente Entscheidungen trifft, die menschliches Denken nachahmen.
Entdecken Sie die fünf Kernphasen der KI-Entwicklung – Daten, Modelle, Training, Feedback und Implementierung – und wie jede Phase intelligentere Ergebnisse ermöglicht.
Verfolgen Sie die Entwicklung der KI von den frühen Theorien der 1950er-Jahre bis zum Aufstieg von Machine Learning, Deep Learning und Generativer KI in den 2020er-Jahren.
Erkunden Sie reale Anwendungsfälle in Branchen wie Gesundheitswesen, Finanzen, Fertigung, Logistik, Bildung und Marketing.
Verstehen Sie die ethischen und regulatorischen Herausforderungen, die die Zukunft der KI prägen – von Bias und Transparenz bis zu Datenschutz, Governance und Nachhaltigkeit.
Erfahren Sie, warum verantwortungsvolle und überprüfbare KI das nächste Jahrzehnt prägen wird – wo Vertrauen, Transparenz und menschliche Zusammenarbeit die Innovation vorantreiben.
Gewinnen Sie Einblicke in die Zukunft der KI (2025–2030) – von algetischer Intelligenz und hybrider Mensch-Maschine-Kooperation bis zu nachhaltigen und dezentralisierten KI-Systemen.
Letztlich soll KI den Menschen nicht ersetzen, sondern sein Potenzial erweitern – für intelligentere Entscheidungen und eine nachhaltigere digitale Welt.
Ein kleines Einzelhandels-Startup verbrachte Monate mit der Entwicklung einer Kunden-App – nur um zuzusehen, wie die Nutzer sie nach dem ersten Login wieder verließen. Nachdem ein KI-gestütztes Empfehlungssystem integriert worden war, verdoppelte sich die Nutzerbindung innerhalb weniger Wochen.
Geschichten wie diese sind heute keine Seltenheit mehr. Künstliche Intelligenz (KI) verändert still und leise, wie Unternehmen arbeiten – von der Prognose von Nachfrage und der Erkennung von Betrug bis hin zur Personalisierung der Gesundheitsversorgung und der Optimierung der Logistik. Doch trotz ihrer rasanten Verbreitung herrscht weiterhin Verwirrung. Viele Fachleute und Studierende fragen sich noch immer: Was genau ist Künstliche Intelligenz, und wie funktioniert sie?
Laut dem Stanford Artificial Intelligence Index Report 2025 hat die weltweite Einführung von KI Rekordwerte erreicht und verändert Branchen sowie Kompetenzanforderungen auf der ganzen Welt.
Dieser Artikel erklärt, was Künstliche Intelligenz wirklich bedeutet – in einfachen, praxisnahen Begriffen. Sie erfahren, wie sie funktioniert, wo sie echten Mehrwert schafft und wie sie die Zukunft von Wirtschaft, Innovation und Alltag gestaltet.
Das Verständnis von Künstlicher Intelligenz: Die wahre Bedeutung hinter dem Begriff
Wenn die meisten von uns den Ausdruck Künstliche Intelligenz (KI) hören, denken wir sofort an Szenen aus Science-Fiction-Filmen: selbstbewusste humanoide Roboter, Maschinen, die die menschliche Intelligenz übertreffen, oder dystopische Welten, in denen Computer die Kontrolle übernehmen.
In Wirklichkeit ist KI jedoch weit weniger dramatisch – und dafür umso praktischer. Sie gestaltet still und leise, wie wir jeden Tag leben und arbeiten.
Was ist KI wirklich? – Ein Blick hinter die technischen Schichten
Im Kern ist Künstliche Intelligenz die Wissenschaft, Maschinen beizubringen, aus Daten zu lernen und Entscheidungen zu treffen, die menschliches Denken widerspiegeln. Es geht nicht darum, Menschen zu ersetzen, sondern ihre Fähigkeiten zu erweitern – Technologie die Möglichkeit zu geben, Muster zu erkennen, sich an neue Informationen anzupassen und Probleme mit intelligenter Präzision zu lösen.
Denken Sie daran, wie Sie täglich Technologie nutzen:
Wenn Netflix Ihnen eine Serie empfiehlt, die zu Ihrer Stimmung passt.
Wenn sich Ihr Smartphone entsperrt, weil es Ihr Gesicht erkennt.
Wenn eine Bank eine verdächtige Transaktion meldet, noch bevor Sie es bemerken.
Das sind keine Zufälle, sondern das Ergebnis von Systemen, die auf Millionen von Interaktionen trainiert wurden, um zu verstehen, was „normal“ ist, und ihre Reaktionen in Echtzeit anzupassen.
Der neue strategische Motor für Unternehmen
In der Geschäftswelt hat sich Künstliche Intelligenz von einer experimentellen Technologie zu einem strategischen Motor für Wachstum und Wettbewerbsfähigkeit entwickelt. Führungskräfte nutzen sie, um die Nachfrage vorherzusagen, Betrug zu erkennen, Lieferketten zu optimieren und personalisierte Kundenerlebnisse zu schaffen. Für Start-ups dient sie als mächtiger Gleichmacher, der kleinen, schlanken Teams ermöglicht, Erkenntnisse und Effizienz zu erreichen, die früher nur großen Unternehmen vorbehalten waren.
Doch KI ist keine einzelne Erfindung oder magische Formel. Sie ist ein Ökosystem aus verschiedenen Disziplinen – Informatik, Mathematik, Linguistik und Psychologie. Gemeinsam schaffen diese Bereiche Systeme, die in der Lage sind zu verstehen, zu schlussfolgern und sich selbst weiterzuentwickeln.
Im Kern ist KI nicht nur Code; sie ist ein lebendiges System aus Daten und Logik, das sich ständig weiterentwickelt. Je mehr Daten sie verarbeitet, desto präziser wird ihr Verständnis – so wie das menschliche Gehirn seine Intelligenz durch Erfahrung stärkt. Wenn sie von menschlicher Zielsetzung geleitet wird, ersetzt KI die menschliche Intelligenz nicht; sie verstärkt sie – und ermöglicht es sowohl Einzelpersonen als auch Organisationen, klügere, schnellere und bedeutungsvollere Entscheidungen zu treffen.
Wie Künstliche Intelligenz funktioniert: Von Daten zu Entscheidungen
Künstliche Intelligenz mag komplex erscheinen, doch im Kern lernt und denkt sie auf erstaunlich ähnliche Weise wie der Mensch. So wie Menschen aus Erfahrungen lernen, lernt KI aus Daten – nur in einem Ausmaß und mit einer Geschwindigkeit, die kein menschlicher Geist erreichen kann.
Jedes intelligente System – vom Chatbot bis zum selbstfahrenden Auto – folgt demselben grundlegenden Lernkreislauf: Daten, Modell, Training, Feedback und Einsatz (Deployment).
1. Daten: Die Grundlage des Lernens
So wie Menschen ihr Verständnis durch Erfahrungen aufbauen, beginnt KI mit Daten – dem digitalen Abbild menschlicher Aktivitäten. Texte, Bilder, Audiodateien und Zahlen speisen den Lernprozess des Systems. Ohne Daten hat KI keinen Kontext, kein Gedächtnis und keine Intelligenz.
Die Qualität der Daten bestimmt die Qualität des Ergebnisses. Saubere, vielfältige und klar gekennzeichnete Datensätze ermöglichen es der KI, sinnvolle Muster zu erkennen – ähnlich wie Ärzte auf präzise Krankenakten angewiesen sind, um zuverlässige Diagnosen zu stellen. In Unternehmen können schlechte oder verzerrte Daten zu falschen Prognosen führen, weshalb moderne Organisationen stark in Data Engineering und Data Governance investieren, um sicherzustellen, dass ihre Erkenntnisse auf einer vertrauenswürdigen Grundlage beruhen.
2. Modelle: Das Gehirn hinter der Maschine
Wenn Daten die Erfahrung darstellen, ist das Modell das Gehirn, das diese Erfahrung interpretiert. Modelle sind mathematische Strukturen, die Maschinen helfen, Muster zu verstehen und über die Welt zu „schließen“.
Ein Beispiel: Ein Modell zur Betrugserkennung im Bankwesen lernt, wie eine „normale“ Transaktion aussieht, und markiert Abweichungen von diesem Muster. Je mehr Transaktionen es verarbeitet, desto besser versteht es, was typisch ist – ähnlich wie menschliche Intuition sich durch Erfahrung schärft.
Moderne Modelle reichen von einfachen Entscheidungsbäumen bis hin zu hochentwickelten Deep Neural Networks, die die Schichtenstruktur des menschlichen Gehirns nachbilden.
3. Training: Daten werden zu Intelligenz
Das Training ist die Phase, in der KI wirklich intelligent wird. Das System analysiert riesige Datensätze, passt interne Parameter an und verbessert sich durch wiederholte Versuche und Fehler. Wie Menschen durch Übung und Feedback ihre Fähigkeiten verfeinern, optimiert KI ihre Algorithmen durch Trainingszyklen.
Der Aufstieg von Machine Learning und Deep Learning hat das Training exponentiell leistungsfähiger gemacht. Laut dem Stanford AI Index Report 2025 erreichten die weltweiten Unternehmensinvestitionen in KI im Jahr 2024 252,3 Milliarden USD, was zeigt, dass KI-Training heute als zentrale Infrastruktur gilt.
Modelle, die auf großen und branchenspezifischen Datensätzen trainiert sind, können inzwischen neue Inhalte generieren, autonome Entscheidungen treffen und sich in Branchen wie Gesundheitswesen oder Logistik flexibel anpassen.
4. Feedback: Lernen aus Fehlern
Kein KI-System ist zu Beginn perfekt. Wie der Mensch lernt es durch Fehler und deren Korrektur. Feedback wirkt dabei wie ein Lehrer, der der KI hilft, ihre Leistung im Laufe der Zeit zu verbessern.
Wenn ein Chatbot eine Kundenanfrage missversteht oder ein Bildklassifikationssystem ein Objekt falsch einordnet, werden diese Fehler zu Lektionen für die nächste Iteration. Kontinuierliche Feedback-Schleifen verfeinern die Genauigkeit und die Übereinstimmung des Modells mit realen Anforderungen. In Unternehmen stammt Feedback oft aus menschlichen Überprüfungen, Nutzerinteraktionen oder automatisierten Monitoringsystemen, die Kennzahlen wie Präzision, Trefferquote und Reaktionszeit verfolgen.
Mit der Zeit wird KI zuverlässiger, nachvollziehbarer und stärker an die Geschäftsziele angepasst – jeder Fehltritt wird zu einer messbaren Verbesserung.
5. Einsatz: Handeln auf Basis von Intelligenz
Sobald ein Modell trainiert und validiert ist, wird es in reale Umgebungen überführt, wo seine Intelligenz konkrete Wirkung entfaltet. Die Implementierung integriert KI-Modelle in operative Systeme wie Finanzüberwachungsplattformen, medizinische Diagnosetools oder industrielle Automatisierungslösungen.
Im Einsatz lernt KI weiter und passt sich an, sobald sie auf neue Daten stößt. Dieser kontinuierliche Lernzyklus verwandelt KI von einem statischen Programm in ein dynamisches System, das sich parallel zur Welt weiterentwickelt, der es dient. Moderne MLOps (Machine Learning Operations)-Frameworks steuern diesen Prozess durch Automatisierung, Überwachung und Governance – und stellen sicher, dass KI effizient, ethisch und regelkonform bleibt.
Der Stanford-Bericht hebt hervor, dass heutige Modelle nicht nur präziser, sondern auch deutlich effizienter sind. Viele neue Architekturen benötigen über hundertmal weniger Rechenleistung als jene von vor wenigen Jahren – bei vergleichbarer Genauigkeit. Dieser Wandel demokratisiert KI und macht fortschrittliche Modelle nicht nur für große Technologieunternehmen, sondern auch für Start-ups und mittelständische Betriebe zugänglich.
Die Entwicklung der Künstlichen Intelligenz: Von der frühen Theorie zur alltäglichen Realität
Künstliche Intelligenz ist nicht über Nacht entstanden. Ihre Entwicklung erstreckt sich über mehr als sieben Jahrzehnte – geprägt von menschlicher Vorstellungskraft, wissenschaftlichem Ehrgeiz und Durchbrüchen, die einstige Theorie in eine der transformativsten Technologien der modernen Zeit verwandelt haben.
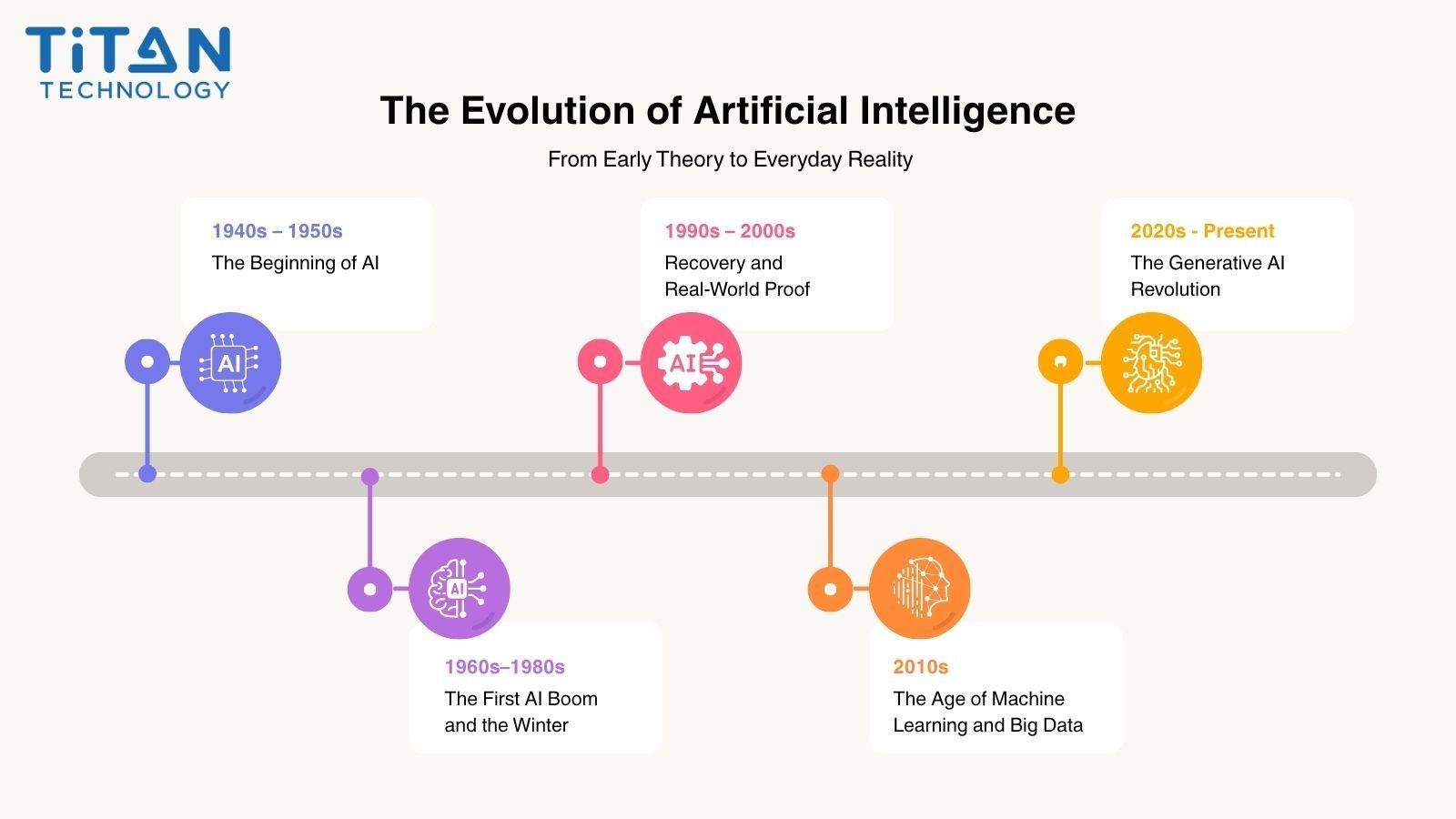
Die Geburt einer Idee (1940er–1950er Jahre)
Das Konzept intelligenter Maschinen entstand lange bevor Computer menschliche Sprache verstehen konnten. 1950 stellte der britische Mathematiker Alan Turing eine Frage, die das Feld über Generationen prägen sollte: Können Maschinen denken? Sein berühmter Turing-Test sollte messen, ob das Verhalten einer Maschine von dem eines Menschen unterscheidbar ist.
Nur wenige Jahre später, 1956, versammelten sich Forscher auf der Dartmouth Conference, wo der Begriff Artificial Itelligence (Künstliche Intelligenz) offiziell eingeführt wurde. Sie waren überzeugt, dass Maschinen lernen, denken und Probleme lösen könnten wie Menschen. Dieser Moment markierte die Geburt einer neuen wissenschaftlichen Ära.
Der erste KI-Boom und der Winter (1960er–1980er Jahre)
Die frühen Jahrzehnte der KI waren geprägt von Begeisterung und Optimismus. Wissenschaftler entwickelten Expertensysteme, die logische Entscheidungen in spezialisierten Bereichen wie Medizin und Ingenieurwesen treffen konnten. Diese Systeme basierten auf sorgfältig programmierten Regeln und zeigten, dass Maschinen menschliches Denken zumindest teilweise nachbilden konnten.
Doch die Technologie jener Zeit war noch nicht bereit, diese hohen Erwartungen zu erfüllen. Computer verfügten weder über genügend Rechenleistung noch über ausreichenden Speicher, um komplexe Denkprozesse zu bewältigen. Die Finanzierung versiegte, und bis Ende der 1970er Jahre ließ das Interesse stark nach – die Ära des ersten KI-Winters begann, geprägt von Skepsis und sinkenden Investitionen.
Erholung und Beweise aus der Praxis (1990er–2000er Jahre)
Mit dem Aufkommen leistungsfähigerer Computer und der weltweiten Vernetzung durch das Internet erlebte die KI eine Wiedergeburt. Größere Datensätze, schnellere Prozessoren und verbesserte Algorithmen ermöglichten es, Probleme zu lösen, die zuvor unerreichbar schienen.
1997 besiegte IBMs Deep Blue den Schachweltmeister Garry Kasparov – ein Beweis dafür, dass Maschinen in strukturierten, strategischen Denkprozessen den Menschen übertreffen können. Zehn Jahre später gewann IBMs Watson die Quizshow Jeopardy! und zeigte, dass KI natürliche Sprache verstehen und aus riesigen Datenmengen präzise Antworten ableiten kann.
Diese Meilensteine markierten einen Wendepunkt: KI war nicht länger nur theoretisch, sondern wurde zur praktischen Realität.
Das Zeitalter von Machine Learning und Big Data (2010er Jahre)
Mit dem Aufstieg von Big Data und Cloud Computing begann eine neue Ära der KI. Machine-Learning- und Deep-Learning-Techniken ermöglichten es Systemen, Muster zu erkennen, Sprache zu übersetzen und Vorhersagen mit bisher unerreichter Genauigkeit zu treffen.
Technologieunternehmen integrierten KI zunehmend in Alltagsprodukte: Sprachassistenten, Empfehlungssysteme, Bilderkennung und prädiktive Analytik wurden Teil des täglichen Lebens. Gleichzeitig machte Cloud-Infrastruktur leistungsstarke KI-Tools für Unternehmen jeder Größe zugänglich – und beschleunigte so ihre Nutzung in verschiedenen Branchen.
Die Revolution der Generativen KI (2020er Jahre)
The 2020s introduced a new chapter in AI history. Generative AI demonstrated that machines could not only analyze data but also create new content. Tools like ChatGPT, Gemini, and DALL·E began producing text, images, and code with human-like fluency, transforming creativity, communication, and productivity.
According to the McKinsey State of AI 2024 report, more than 70 percent of global organizations now use AI in at least one business function, nearly doubling the adoption rate from five years earlier. Global investment in generative AI continues to surge, reflecting its growing role as both a creative and analytical engine for modern enterprises.
This period also brought new challenges and responsibilities. As AI systems became more autonomous and capable, questions around ethics, transparency, and accountability came to the forefront. Businesses and governments worldwide began focusing not only on innovation but also on the responsible governance of AI technologies.
Alltägliche Realität: Intelligenz überall
Heute hat KI das Forschungslabor längst verlassen und ist Teil des täglichen Lebens geworden. Sie filtert Spam aus E-Mails, sagt Wartungsbedarfe in Fabriken voraus, unterstützt Ärzte bei der Diagnostik und treibt Anwendungen an, die Sprache und Bilder verstehen.
Die Grenze zwischen der Nutzung von Technologie und der Zusammenarbeit mit Intelligenz verschwimmt zunehmend. Was einst wie Science-Fiction klang, ist heute eine unsichtbare Infrastruktur, die Entscheidungen unterstützt, Automatisierung antreibt und Erlebnisse über Branchen hinweg personalisiert.
Künstliche Intelligenz hat sich von einer Frage – Können Maschinen denken? – zu einer Antwort entwickelt, die die Art und Weise verändert, wie die Menschheit innoviert, lernt und sich verbindet.
Ihre Entwicklung spiegelt nicht nur Fortschritte in Algorithmen und Rechenleistung wider, sondern auch den fortwährenden menschlichen Antrieb, Technologien zu schaffen, die das Verständnis vertiefen und neue Möglichkeiten eröffnen.
Zentrale Anwendungsbereiche der Künstlichen Intelligenz im Jahr 2025 und darüber hinaus
Künstliche Intelligenz hat sich von einem Forschungskonzept zu einer praktischen Kraft entwickelt, die Innovation und Effizienz in allen Branchen vorantreibt. Im Jahr 2025 reicht ihr Einfluss weit über Automatisierung hinaus – sie verändert grundlegend, wie Unternehmen Entscheidungen treffen, Kunden bedienen und in einer zunehmend datengetriebenen Welt Wert schaffen. Während Organisationen in ihrer digitalen Transformation reifen, entwickelt sich KI von experimentellen Projekten zu unternehmensweiten Strategien, die langfristige Wettbewerbsfähigkeit bestimmen.
Gesundheitswesen: Präzisere Diagnostik und vorausschauende Versorgung
KI revolutioniert das Gesundheitswesen, indem sie Präzision erhöht, Diagnosefehler reduziert und die Entdeckung neuer Therapien beschleunigt. Maschinelles Lernen ermöglicht es, Krankheiten wie Krebs oder Herz-Kreislauf-Erkrankungen in frühen Stadien zu erkennen – was Ärzten erlaubt, früher einzugreifen und Behandlungsergebnisse zu verbessern. Krankenhäuser nutzen zudem prädiktive Analysen, um Patienten mit Rückfallrisiko zu identifizieren, Ressourcen effizienter einzusetzen und die Versorgungsqualität zu steigern.
Aktuelle Fachstudien zeigen, dass KI-gestützte Diagnosetools die Genauigkeit erhöhen und die Auswertungszeit in Radiologie und Pathologie verkürzen. Pharmaunternehmen wenden generative KI an, um molekulare Wechselwirkungen zu simulieren, wodurch sich die Entwicklungszeit neuer Medikamente von Jahren auf Monate verkürzen lässt. Das Ergebnis: schnellere Innovation, geringere Kosten und individuellere Behandlungen.
Finanzwesen: Risikomanagement und Betrugserkennung
Im Finanzsektor definiert KI neu, wie Institutionen Risiken steuern und Vertrauen sichern. Banken und Fintech-Unternehmen setzen maschinelles Lernen ein, um betrügerische Aktivitäten in Echtzeit zu erkennen – sie analysieren Millionen von Transaktionen und markieren Anomalien, die menschlichen Analysten entgehen könnten. Prognostische Kreditscoring-Systeme fördern Transparenz und verringern Verzerrungen bei Kreditentscheidungen, während KI-Chatbots schnelleren und konsistenteren Kundenservice bieten.
Laut der McKinsey Global AI Survey 2025 Berichten Finanzinstitute, die KI in ihre Kernprozesse integriert haben, von bis zu 30 % höherer Erkennungsrate bei Betrug und 20 % schnelleren Compliance-Prüfungen.
Da Finanzökosysteme zunehmend komplexer werden, entwickelt sich KI von einer reaktiven Schutzmaßnahme zu einem proaktiven Governance-Instrument, das Risiken erkennt, bevor sie eskalieren.
Fertigung: Intelligente Automatisierung und vorausschauende Wartung
In der Industrie ist KI das Fundament von Industrie 4.0. Durch die Kombination von maschinellem Lernen und dem Internet of Things (IoT) werden Fabriken intelligenter, anpassungsfähiger und selbstoptimierend. Predictive Maintenance ermöglicht es Maschinen, potenzielle Ausfälle frühzeitig zu erkennen, wodurch Stillstände reduziert und Millionen an Betriebskosten eingespart werden.
Computer Vision-Technologien übernehmen die Echtzeit-Qualitätskontrolle, um sicherzustellen, dass Produkte höchste Standards erfüllen, ohne die Produktion zu verlangsamen. KI-gesteuerte Roboter übernehmen repetitive oder gefährliche Aufgaben mit Präzision und Sicherheit, während Mitarbeiter sich auf kreative und strategische Tätigkeiten konzentrieren können. In den kommenden Jahren wird KI zudem eine Schlüsselrolle in der Nachhaltigkeit spielen – sie hilft Herstellern, Abfall und Energieverbrauch zu minimieren, ohne Produktivität einzubüßen.
Logistik und Lieferketten: Echtzeit-Optimierung
Lieferketten sind keine starren Netzwerke mehr, sondern dynamische Ökosysteme, die ständige Sichtbarkeit und Anpassungsfähigkeit erfordern.KI liefert die Intelligenz, die diese Systeme am Laufen hält – von vorausschauender Nachfrageplanung über Routenoptimierung in Echtzeit bis hin zu automatisierter Bestandsführung. So können Unternehmen schneller auf Marktschwankungen und Störungen reagieren.
In der Logistik steuern KI-Systeme Flotten, prognostizieren Lieferverzögerungen und navigieren autonome Fahrzeuge in Lagern. Diese Koordination senkt Emissionen, reduziert Kosten und verbessert die Lieferzuverlässigkeit. Das Ergebnis ist eine neue Ära adaptiver Lieferketten, die kontinuierlich lernen und sich optimieren – und so die Widerstandsfähigkeit in einem volatilen globalen Markt stärken.
Bildung und Arbeitswelt: Personalisierte und lebenslange Weiterbildung
KI verändert die Art und Weise, wie Menschen lernen, grundlegend. Intelligente Tutoring-Systeme analysieren Leistungsdaten und passen Lerninhalte in Echtzeit an die Stärken und Schwächen der Lernenden an. In Hochschulen und Unternehmen erkennen KI-Tools Kompetenzlücken und empfehlen maßgeschneiderte Lernpfade, um Mitarbeiter auf neue Rollen in der digitalen Wirtschaft vorzubereiten.
Generative KI entwickelt sich zudem zu einem persönlichen Lernbegleiter – sie unterstützt bei der Inhaltserstellung, Übersetzung und interaktiven Problemlösung. Bildung wird dadurch zugänglicher, datenbasierter und individueller. Der Fokus verlagert sich von standardisiertem Unterricht hin zu kontinuierlichem Lernen, das sich parallel zu Technologie und Marktanforderungen weiterentwickelt.
Marketing und Kundenerlebnis: Relevanz im großen Maßstab
KI ermöglicht es Marken, Kundenbedürfnisse mit nie dagewesener Genauigkeit zu verstehen und vorherzusehen.
Durch die Kombination von Verhaltensanalyse, Stimmungserkennung und prognostischer Modellierung können Marketer hyperpersonalisierte Erlebnisse in großem Maßstab bieten.
Empfehlungssysteme und generative KI verändern, wie Kampagnen konzipiert werden – von Textgestaltung bis hin zu visuellen Elementen – und sorgen dafür, dass jede Interaktion relevant und zeitgerecht wirkt.
Da KI-Systeme Zugang zu umfangreicheren Daten erhalten, verschiebt sich der Fokus von kurzfristigen Konversion-Zielen hin zu authentischen, vertrauensbasierten Beziehungen. Verantwortungsbewusster Umgang mit Daten und transparente KI-Modelle werden zu entscheidenden Differenzierungsmerkmalen für Marken, die langfristige Loyalität aufbauen wollen.
Einblicke: Von Automatisierung zu Intelligenz
In allen Branchen liegt der tiefgreifendste Einfluss der Künstlichen Intelligenz nicht darin, menschliche Arbeit zu ersetzen, sondern menschliches Potenzial zu verstärken. KI entwickelt sich von einem Werkzeug der Automatisierung zu einer strategischen Intelligenzschicht, die Entscheidungsfindung verbessert, Innovation beschleunigt und Wettbewerbsfähigkeit stärkt.
Während wir uns weiter in Richtung 2026 und darüber hinaus bewegen, lautet die zentrale Frage nicht mehr, was KI leisten kann, sondern wie verantwortungsvoll sie gesteuert werden kann. Organisationen, die Innovation mit Transparenz und Ethik verbinden, werden das nächste Kapitel der intelligenten Transformation anführen – eine Zukunft, in der Technologie nicht nur der Effizienz dient, sondern auch dem Vertrauen und dem menschlichen Fortschritt.
Herausforderungen und ethische Überlegungen in der Künstlichen Intelligenz
Während Künstliche Intelligenz immer tiefer in Wirtschaft und Gesellschaft integriert wird, gehen ihre potenziellen Vorteile mit ebenso bedeutenden Herausforderungen einher. Die nächste Phase des KI-Fortschritts wird sich nicht nur auf technologische Fähigkeiten konzentrieren, sondern auch auf moralische und operative Verantwortung. Vertrauen in KI hängt heute davon ab, wie effektiv Organisationen Themen wie Voreingenommenheit, Transparenz, Sicherheit und Nachhaltigkeit angehen.
Voreingenommenheit und Fairness
KI-Systeme lernen aus Daten, und diese Daten spiegeln die menschliche Geschichte mit all ihren Unvollkommenheiten wider. Wenn Trainingsdaten soziale, wirtschaftliche oder kulturelle Verzerrungen enthalten, kann das System unbeabsichtigt Ungleichheit verstärken. So haben beispielsweise Rekrutierungsalgorithmen, die auf historischen Einstellungsdaten trainiert wurden, gezeigt, dass sie bestimmte Bevölkerungsgruppen gegenüber anderen bevorzugen – und damit vergangene Vorurteile fortsetzen, anstatt sie zu korrigieren.
Fairness zu gewährleisten erfordert mehr als nur vielfältige Datensätze. Es verlangt bewusste Designentscheidungen, kontinuierliche Überwachung und inklusive Governance. In den letzten Jahren haben Organisationen begonnen, Rahmenwerke für ethische KI-Modelle einzuführen, die Erklärbarkeit, vielfältige Stichproben und Bias-Tests priorisieren. Diese Maßnahmen helfen KI-Systemen, Entscheidungen zu treffen, die sowohl präzise als auch gerecht sind – und bekräftigen das Prinzip, dass Technologie allen Menschen dienen sollte, nicht nur wenigen.
Transparenz und Nachvollziehbarkeit
Eine der größten Herausforderungen bei der Einführung von Künstlicher Intelligenz ist das sogenannte „Black-Box“-Problem – Systeme, die zwar präzise Ergebnisse liefern, aber nicht offenlegen, wie diese zustande kommen. Da KI zunehmend Entscheidungen im Gesundheitswesen, im Finanzsektor und in der Verwaltung beeinflusst, wird die Nachvollziehbarkeit zu einer moralischen wie auch rechtlichen Verpflichtung.
Erklärbare KI (Explainable AI, XAI) soll diese Lücke schließen, indem sie Einblicke in die Entscheidungsprozesse von Algorithmen bietet. Indem der Denk- und Analyseprozess sichtbar gemacht wird, hilft XAI den Nutzern, die Logik hinter Empfehlungen zu verstehen, stärkt das Vertrauen in automatisierte Systeme und ermöglicht es Regulierungsbehörden, die Einhaltung von Vorschriften zu bewerten. In den kommenden Jahren wird Transparenz nicht nur das Vertrauen fördern, sondern auch darüber entscheiden, ob KI-Lösungen von der Öffentlichkeit akzeptiert oder abgelehnt werden.
Datenschutz und Sicherheit
KI lebt von Daten, doch ihre Abhängigkeit von großen und sensiblen Datensätzen bringt erhebliche Risiken für Datenschutz und Sicherheit mit sich. Von Gesundheitsakten bis hin zu Finanztransaktionen – Daten treiben die Algorithmen an, die Erkenntnisse und Automatisierung ermöglichen. Ohne geeignete Kontrollmechanismen können sie jedoch auch zu Datenpannen, Missbrauch und Vertrauensverlust führen.
Regierungen und Organisationen reagieren darauf, indem sie Datenschutzrahmen stärken. Vorschriften wie die EU-Datenschutz-Grundverordnung (GDPR) und der kommende EU AI Act schaffen klarere Standards für Datenerhebung, Einwilligung und Modellverantwortung. Auch in Asien und im Nahen Osten entstehen neue nationale Rahmenwerke, die darauf abzielen, Innovation und Datenschutz in Einklang zu bringen. Die Zukunft der KI wird davon abhängen, wie gut es Unternehmen gelingt, Datenintegrität zu wahren und gleichzeitig personalisierte, datenbasierte Erlebnisse zu bieten.
Regulierung und globale Governance
Das kommende Jahrzehnt wird die globalen Regeln für eine verantwortungsvolle Künstliche Intelligenz definieren. Im Jahr 2025 wird das KI-Gesetz der Europäischen Union (EU AI Act) vollständig in Kraft treten. Es führt ein risikobasiertes Rahmenwerk ein, das KI-Systeme je nach ihrer gesellschaftlichen Auswirkung von minimalem bis hohem Risiko klassifiziert. Gleichzeitig spiegeln der NIST AI Risk Management Framework (RMF) in den Vereinigten Staaten sowie ähnliche Initiativen in den VAE, in Singapur und in Japan eine weltweite Bewegung hin zu einer harmonisierten Governance wider.
Regulierung wird heute nicht mehr als Einschränkung betrachtet, sondern als Ermöglicher von Vertrauen. Klare Standards schaffen faire Wettbewerbsbedingungen, unter denen Innovation und Sicherheit nebeneinander bestehen können. Unternehmen, die sich proaktiv an diese Rahmenwerke anpassen, sichern sich nicht nur die Einhaltung gesetzlicher Vorschriften, sondern auch einen strategischen Vorteil – indem sie Technologien entwickeln, denen sowohl Kunden als auch Aufsichtsbehörden vertrauen.
Arbeitswelt im Wandel und Kompetenzentwicklung
KI-gestützte Automatisierung verändert den globalen Arbeitsmarkt, indem sie manche Aufgaben eliminiert und gleichzeitig völlig neue Rollen schafft, die technologische und menschliche Fähigkeiten verbinden. Laut dem World Economic Forum wird bis 2030 fast die Hälfte aller Beschäftigten eine umfassende Weiter- oder Umschulung benötigen, um relevant zu bleiben.
Vorausschauende Unternehmen reagieren mit KI-Schulungsprogrammen und adaptiven Lerninitiativen, die Mitarbeiter befähigen, sich parallel zur Technologie weiterzuentwickeln. Die Zukunft der Arbeit wird sich stärker auf Kreativität, kritisches Denken und Zusammenarbeit konzentrieren – Fähigkeiten, die KI ergänzen, statt mit ihr zu konkurrieren. Erfolgreiche Unternehmen werden jene sein, die Talententwicklung nicht als Kostenfaktor, sondern als strategische Investition in Resilienz betrachten.
Nachhaltigkeit und Umweltbelastung
Hinter jedem KI-Modell steht immense Rechenleistung – und damit ein erheblicher Energieverbrauch.
Das Training großskaliger Modelle erzeugt einen spürbaren CO₂-Fußabdruck und wirft Fragen nach den ökologischen Kosten des digitalen Fortschritts auf.
Die Forschung zu „Green AI“ gewinnt an Dynamik – mit Schwerpunkten auf energieeffizienten Algorithmen, optimierten Modellarchitekturen und Rechenzentren, die mit erneuerbarer Energie betrieben werden.
Unternehmen beginnen, die ökologische Bilanz ihrer KI-Aktivitäten als Teil umfassender Nachhaltigkeitsziele zu messen. Die nächste Generation von KI-Führungskräften wird sich nicht nur durch Geschwindigkeit oder Genauigkeit auszeichnen, sondern durch Innovationen, die die Grenzen des Planeten respektieren.
Einblicke: Von ethischem Bewusstsein zu strategischer Verantwortung
Die wahre Herausforderung der Künstlichen Intelligenz in den Jahren 2025 und darüber hinaus liegt nicht in der technischen Beherrschung, sondern in der moralischen Reife. Da KI zunehmend zur unsichtbaren Infrastruktur globalen Fortschritts wird, muss sich Ethik von einer reinen Compliance-Aufgabe zu einer strategischen Priorität entwickeln. Rahmenwerke wie der EU AI Act und das NIST RMF bieten die Grundlage für verantwortungsvolle Praxis – doch echte Verantwortung entsteht aus der Unternehmenskultur: aus Führungspersönlichkeiten, die Transparenz, Fairness und menschenzentriertes Design zu ihren Leitprinzipien machen.
Für zukunftsorientierte Unternehmen ist verantwortungsvolle KI kein Hindernis, sondern ein Wettbewerbsvorteil.
Vertrauenswürdige Systeme fördern Zuversicht, ziehen Investitionen an und sichern langfristigen Erfolg.
Indem Innovation mit Integrität verbunden wird, kann KI nicht nur die Unternehmensleistung stärken, sondern auch Gesellschaft und Umwelt positiv beeinflussen.
Ausblick: Die Zukunft der Künstlichen Intelligenz (2025–2030)
Die Künstliche Intelligenz tritt in ihr transformativstes Jahrzehnt ein. Zwischen 2025 und 2030 wird sie sich von einer sichtbaren Technologie zu einer unsichtbaren Infrastruktur entwickeln, die stillschweigend Volkswirtschaften antreibt, Branchen umgestaltet und beeinflusst, wie Menschen arbeiten, lernen und sich vernetzen. Die entscheidende Frage der Zukunft lautet nicht mehr, was KI leisten kann – sondern wie verantwortungsvoll und nachhaltig sie eingesetzt wird.
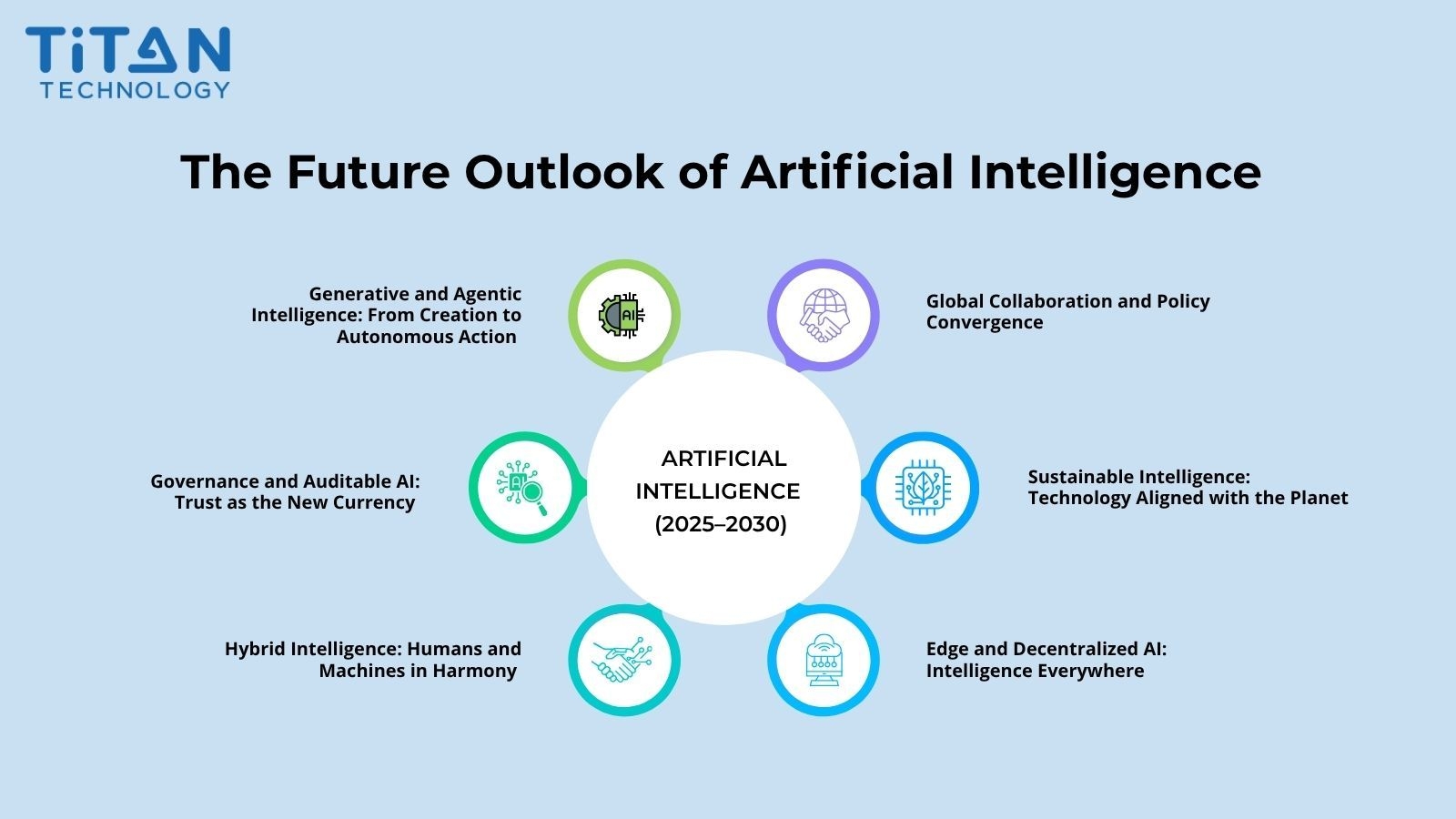
Generative und Agentische Intelligenz: Von der Schöpfung zur autonomen Handlung
Generative KI hat bereits ihre Fähigkeit bewiesen, Texte, Bilder und Code mit menschenähnlicher Sprachgewandtheit zu erstellen. Die nächste Grenze ist die agentische Intelligenz – KI-Systeme, die nicht nur Inhalte generieren, sondern auch autonom handeln. Diese intelligenten Agenten können planen, argumentieren und komplexe Aufgaben in vernetzten Umgebungen ausführen.
In der Unternehmenslandschaft bedeutet diese Entwicklung, dass KI sich von der Unterstützung von Arbeitsabläufen zur Orchestrierung dieser Abläufe bewegt. Zukünftige Systeme werden Betriebsabläufe in Echtzeit überwachen, Empfehlungen aussprechen und sogar im Namen von Menschen handeln, wenn Präzision und Geschwindigkeit entscheidend sind. Unternehmen, die das Gleichgewicht zwischen Autonomie und Aufsicht meistern, werden einen entscheidenden Wettbewerbsvorteil erlangen und Intelligenz in einen echten strategischen Partner verwandeln, anstatt sie nur als Hintergrundwerkzeug zu betrachten.
Governance und prüfbare KI: Vertrauen als neue Währung
Da KI tief in Entscheidungen eingebettet wird, die Leben beeinflussen, wird Verantwortlichkeit zum entscheidenden Maßstab für Vertrauen. Die nächsten fünf Jahre werden den Aufstieg der prüfbaren KI erleben – Systeme, die so konzipiert sind, dass sie ihre Entscheidungsprozesse erklären, ihre Datenquellen nachverfolgen und ihre Ergebnisse in einer Weise begründen können, die sowohl für Regulierungsbehörden als auch für nicht-technische Nutzer verständlich ist.
Ähnlich wie bei Finanzprüfungen werden diese Mechanismen sicherstellen, dass KI-Entscheidungen transparent und nachvollziehbar sind. Organisationen, die überprüfbare KI-Governance übernehmen, werden öffentliches Vertrauen gewinnen, ethische Investoren anziehen und ihre Widerstandsfähigkeit gegenüber regulatorischen Risiken stärken. In dieser neuen Ära wird Vertrauen die wertvollste Währung des technologischen Fortschritts sein.
Hybride Intelligenz: Menschen und Maschinen in Harmonie
Die Zukunft der Arbeit wird nicht durch den Wettbewerb zwischen Menschen und Maschinen definiert, sondern durch Zusammenarbeit. Hybride Intelligenz verbindet menschliche Kreativität, Empathie und ethisches Urteilsvermögen mit der analytischen Präzision und Skalierbarkeit der KI.
Die Entscheidungsfindung in Vorstandsräumen, Fabriken und Forschungslaboren wird zunehmend von dieser Partnerschaft geprägt sein. Menschen liefern Kontext und Gewissen, während KI Erkenntnisse und Geschwindigkeit bereitstellt. Gemeinsam werden sie Entscheidungsökosysteme bilden, die in der Lage sind, komplexe globale Herausforderungen zu lösen – von Nachhaltigkeit bis hin zu Innovationen im Gesundheitswesen.
Edge- und Dezentralisierte KI: Intelligenz überall
Bis 2030 wird Künstliche Intelligenz nicht mehr ausschließlich auf große, zentrale Rechenzentren angewiesen sein. Edge-KI – Intelligenz, die direkt auf Geräten, Sensoren und lokalen Systemen arbeitet – wird Echtzeitentscheidungen dort ermöglichen, wo Daten entstehen.
Diese Veränderung wird Datenschutz verbessern, Latenzzeiten verringern und neue Möglichkeiten in Bereichen wie intelligenter Fertigung, Logistik und personalisierter Gesundheitsversorgung eröffnen. Fortschritte in Konnektivität und Quantencomputing werden diese Dezentralisierung weiter verstärken und es Organisationen ermöglichen, Intelligenz mit der Geschwindigkeit des Geschäfts einzusetzen. Das Ergebnis wird eine Welt sein, in der KI überall und dennoch unaufdringlich ist – nahtlos eingebettet in die Systeme, von denen wir täglich abhängen.
Nachhaltige Intelligenz: Technologie im Einklang mit dem Planeten
Die Umweltkosten der KI sind nicht mehr zu übersehen. Da Modelle größer und komplexer werden, verbrauchen sie enorme Mengen an Rechenleistung und Energie. Die nächste Innovationsära wird durch nachhaltige Intelligenz geprägt sein, die auf energieeffiziente Architekturen, mit erneuerbaren Energien betriebene Rechenzentren und algorithmische Optimierung setzt.
Unternehmen messen bereits den CO₂-Fußabdruck ihrer KI-Aktivitäten und erforschen „grüne KI“-Ansätze, die Abfall minimieren und gleichzeitig die Leistung beibehalten. In den kommenden Jahren wird Führung in der KI nicht nur durch Fähigkeiten, sondern auch durch Gewissen definiert. Organisationen, die verantwortungsbewusst innovieren, werden eine Zukunft gestalten, in der Fortschritt und Nachhaltigkeit gemeinsam voranschreiten.
Globale Zusammenarbeit und politische Annäherung
Künstliche Intelligenz ist mittlerweile eine gemeinsame globale Infrastruktur, die Grenzen überschreitet. Der Weg in die Zukunft wird von der Zusammenarbeit zwischen Regierungen, Unternehmen und der Wissenschaft abhängen, um harmonisierte Standards für Sicherheit, Fairness und Transparenz zu schaffen.
Regionen wie die Europäische Union, Nordamerika und Asien Unternehmen bereits Schritte in Richtung einer politischen Angleichung. Die erfolgreichsten Organisationen werden diejenigen sein, die diese Konvergenz annehmen und flexible Compliance-Modelle einführen, die globale ethische Prinzipien respektieren und gleichzeitig ein hohes Maß an Innovationsgeschwindigkeit beibehalten. Governance wird nicht länger als Bürokratie betrachtet, sondern als Rückgrat langfristigen digitalen Vertrauens.
Einblick: Das Jahrzehnt verantwortungsvoller Intelligenz
Das kommende Jahrzehnt wird nicht dadurch definiert, wie mächtig Künstliche Intelligenz wird, sondern wie weise die Menschheit sie nutzt. Der Maßstab für Fortschritt wird sich von Fähigkeit zu Verantwortung verschieben.
Die Organisationen, die florieren werden, sind diejenigen, die Ethik, Nachhaltigkeit und menschliche Werte in jede Phase des KI-Designs und der Implementierung integrieren. Dies ist das Zeitalter der verantwortungsvollen Intelligenz – eine Zeit, in der Innovation nicht nur dem Unternehmenswachstum dient, sondern auch dem gesellschaftlichen Vertrauen und dem Gleichgewicht unseres Planeten.
Für visionäre Unternehmen ist dies keine Einschränkung, sondern eine Chance. Durch die Verbindung von Innovation und Integrität können Unternehmen eine globale Bewegung anführen, in der Technologie das menschliche Potenzial stärkt und eine intelligentere, sicherere und gerechtere Welt aufbaut.
Schlussfolgerung: Eine Zukunft verantwortungsvoller Intelligenz gestalten
Künstliche Intelligenz ist nicht mehr nur eine Technologie; sie ist Teil unseres Lebens, unserer Entscheidungen und unserer Träume geworden. Von der Automatisierung bis zur Förderung von Kreativität berührt KI heute jede Dimension des modernen Lebens. Doch das wahre Maß des Fortschritts liegt nicht darin, was Maschinen tun können, sondern wie weise Menschen sie nutzen.
Das nächste Kapitel der KI wird von Menschen geschrieben – von denen, die Intelligenz mit Empathie, Fairness und Vision lenken. Vertrauen und Transparenz werden die Zukunft stärker prägen als Geschwindigkeit oder Größe.
Bei Titan Technology Corporation glauben wir, dass Intelligenz immer der Menschheit dienen sollte. Wenn Ethik und Nachhaltigkeit Innovation leiten, wird Technologie mehr als nur ein Werkzeug für Effizienz – sie wird zu einem Partner beim Aufbau einer intelligenteren, sichereren und mitfühlenderen Welt.